Third Party Maintenance
Next-Gen Data Center Support
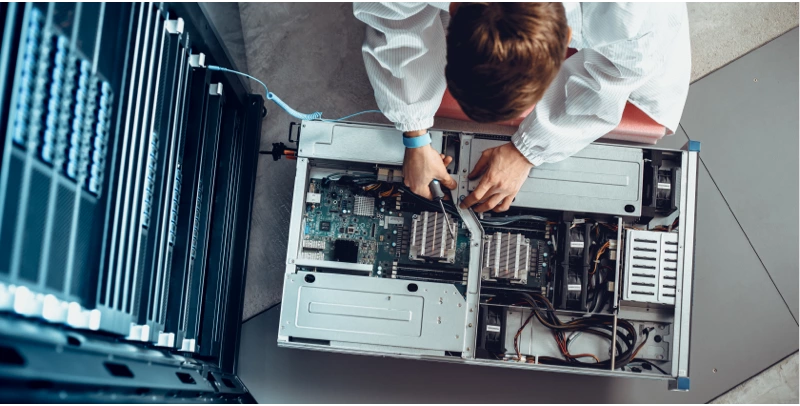
Data Center Hardware Maintenance
What’s next-gen support? It’s an altogether new tier of maintenance for storage maintenance, server support and network hardware support.
One that’s unmatched by ordinary TPMs and even the OEMs. It’s proactive monitoring, 24/7 L3 support, self-service via a mobile app, the industry’s only First-Time Fix™ Guarantee and more.
Supported OEMs
Why Move Your Hardware Support to Park Place?
-
One Partner Across OEMs, Across the World
- With multi-vendor hardware support provided in ~180 countries you can simplify IT maintenance by reducing the number of partners you need.
-
Extend the Life of Hardware
- End of Service Life (EOSL) support keeps your investments up and running longer, maximizing ROI and freeing money for other initiatives.
-
Fully Automated Maintenance Experience
- ParkView Hardware Monitoring™ monitors for incidents 24/7 and automatically opens tickets, triages the issue and dispatches IT support.
-
Follow-the-Sun Support in 170 Languages
- Wherever you are, and whenever the need arises, Park Place is there with our multi-lingual customer support (including L3 support).
-
The Industry’s Only First-Time Fix Guarantee™
- If a return trip is needed to fix the same issue on the same device within 5 days, you get one month of support on the device free.
-
30-40% Less than the OEM
- Park Place combines the confidence that comes from the industry leader supporting 21,500+ customers and SLAs similar to the OEM with significant cost savings.
The Next-Gen Data Center Support Experience
-
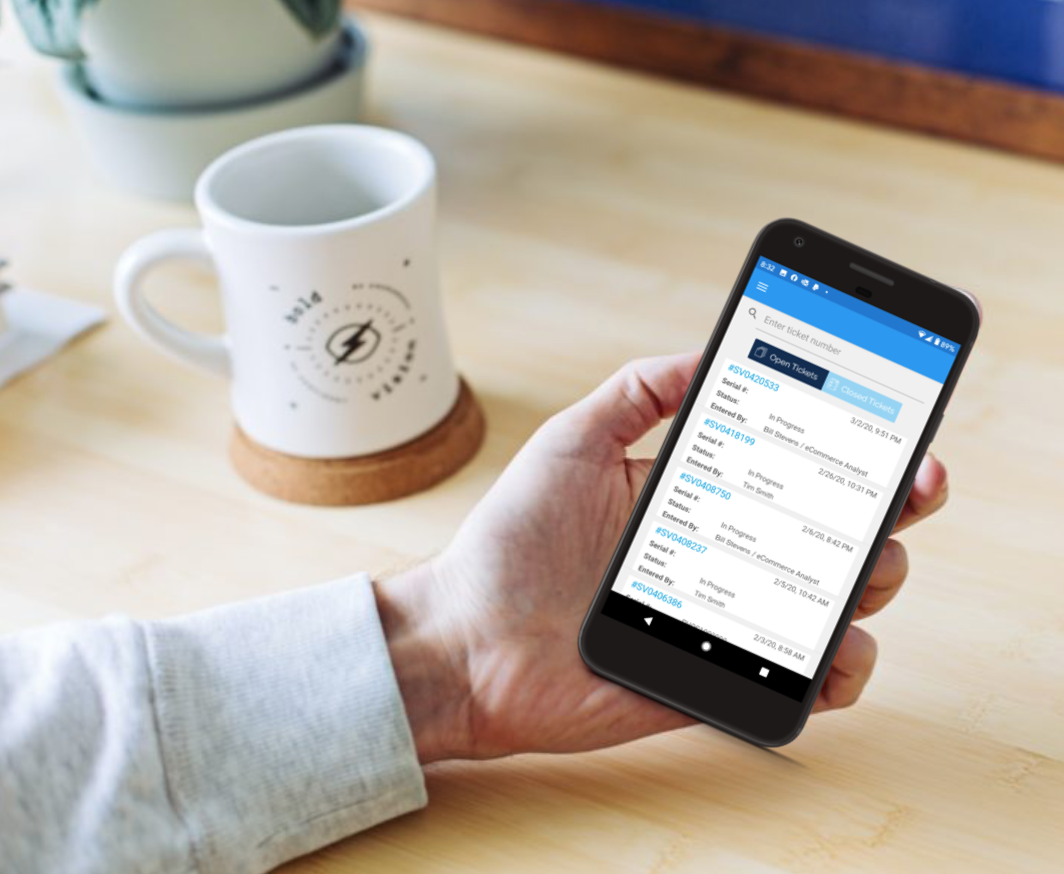
Self-Service Management
The Central Park Customer Portal is an innovative single pane of glass for managing your data center maintenance & monitoring. Key features include:
- Easy-to-read dashboard of key metrics
- Service ticket, contract and asset management
- Multi-account access
- Ability to designate multiple customer administrators
- ParkView™ Hub including installation wizard and visibility to monitor devices
- Accessible via PPTechMobile App
- 24-hour live chat
-
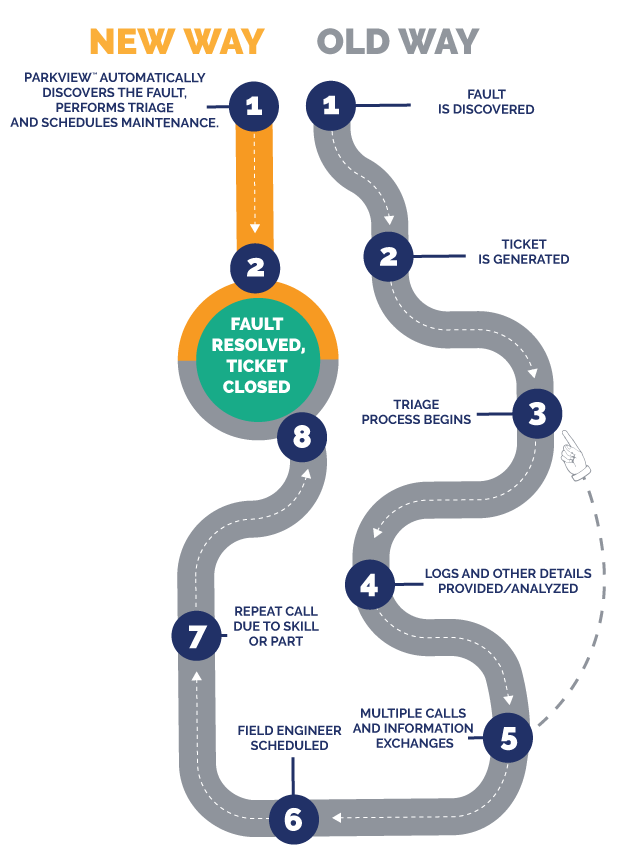
Proactive Monitoring
Whether you’re monitoring Storage, Server, or Network devices, ParkView Hardware Monitoring™ reduces the number of touchpoints between you and a maintenance solution to two easy steps by proactively identifies faults 24/7 without the need for customer action of any kind.
-
First-Time Fix™ Guarantee
A lot of maintenance providers claim to have a high first-time fix rate but only one puts their reputation on the line – Park Place Technologies. With our First-Time Fix™ Guarantee if we don’t resolve your storage, server or network hardware issue on the first visit, we’ll credit you for one month of maintenance (and monitoring if applicable) on that device. It’s that simple.
-
Fully Integrated Approach
With a full suite of infrastructure management services and data center professional services, Park Place Technologies can help you optimize your data center support beyond typical break-fix maintenance offered by ordinary TPMs.
Been There, Fixed That.
-
~180Countries serviced
-
900+Spare parts locations
-
21,500+Current customers supported

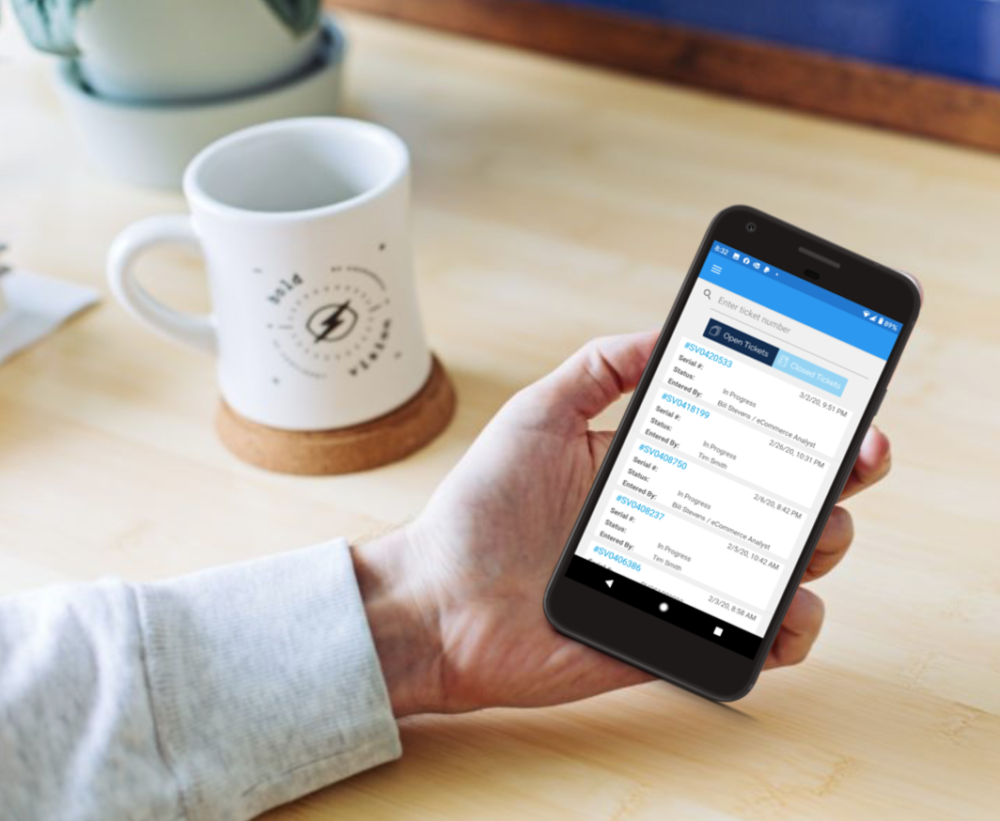
Central Park Customer Portal
- Easy-to-read dashboard of key metrics
- Service ticket, contract and asset management
- Multi-account access
- Ability to designate multiple customer administrators
- ParkView™ Hub including installation wizard and visibility to monitor devices
- Accessible via PPTechMobile App.
- 24-hour live chat
Engineer Expertise
-
600+Global Professionals
-
15+Years Average Experience
-
150K+Service Calls 2021